The internal organs, called the visceral organs, are located within specific body cavities. The two main cavities are the dorsal cavity and the larger ventral cavity. The dorsal cavity can be subdivided into two parts: The cranial cavity within the skull contains the brain; and the spinal cavity, protected by the vertebrae, contains the spinal cord.
The ventral cavity is subdivided into the thoracic (thoras'ik) cavity and the abdominopelvic cavity. Membranes divide the thoracic cavity into the pleural cavities, containing the right and left lungs, and the pericardial cavity, containing the heart. Th e mediastinum (me" de-ah -sti' n urn) is the mass of tissues and organs between the pleural cavities. The thoracic cavity is separated from the abdominopelvic cavity by a horizontal muscle called the diaphragm.
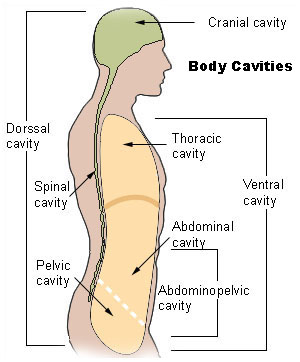 The abdominopelvic cavity has two portions: the upper abdominal cavity and the lower pelvic cavity. The stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and most of the small and large intestines are in the abdominal cavity. The pelvic cavity contains the rectum, the urinary bladder, the internal reproductive organs, and the rest of the large intestine. Males have an external extension of the abdominal wall, called the scrotum, where the testes are found.
The abdominopelvic cavity has two portions: the upper abdominal cavity and the lower pelvic cavity. The stomach, liver, spleen, gallbladder, and most of the small and large intestines are in the abdominal cavity. The pelvic cavity contains the rectum, the urinary bladder, the internal reproductive organs, and the rest of the large intestine. Males have an external extension of the abdominal wall, called the scrotum, where the testes are found.The abdomen can be divided into four quadrants by running a transverse plane across the midsagittal plane at the point of the navel. Physicians commonly use these quadrants to identify the locations of patients' symptoms. The four quadrants are: (1) right upper (right superior) quadrant, (2) left upper (left superior) quadrant, (3) right lower (right inferior) quadrant, and (4) left lower (left inferior) quadrant.
The abdominopelvic cavity can also be divided into nine regions. These regions are:
Umbilical, which is centrally located and surrounds the umbilicus (navel)
Lumbar, which are the regions to the right and left of the umbilical region (the term lumbar refers to the lower back, which occurs here)
Epigastric (epi-, above; gastric, stomach), which is the central region superior to the umbilical region
Hypochondriac (hypo-, under; chondral, cartilage), which are the regions to the right and left of the epigastric region and which are inferior to the cartilage of the rib cage
Hypogastric, which is the central region inferior to the umbilical region
Iliac, which are the regions to the right and left of the hypogastric region (the term iliac refers to the iliac [hip] bones that occur here)
